Lithopsspp.
Have you ever jest about wanting a preferred rock and roll ? How about aliving stone , alternatively ? And yes , I ’m speak about farm lithops succulent plants !
Masters of mimicry , living Harlan Fiske Stone are fascinating succulents , but these quirky little flora also have quirky little care routines .
We link to vendors to help you find relevant merchandise . If you corrupt from one of our links , we may earn a commission .

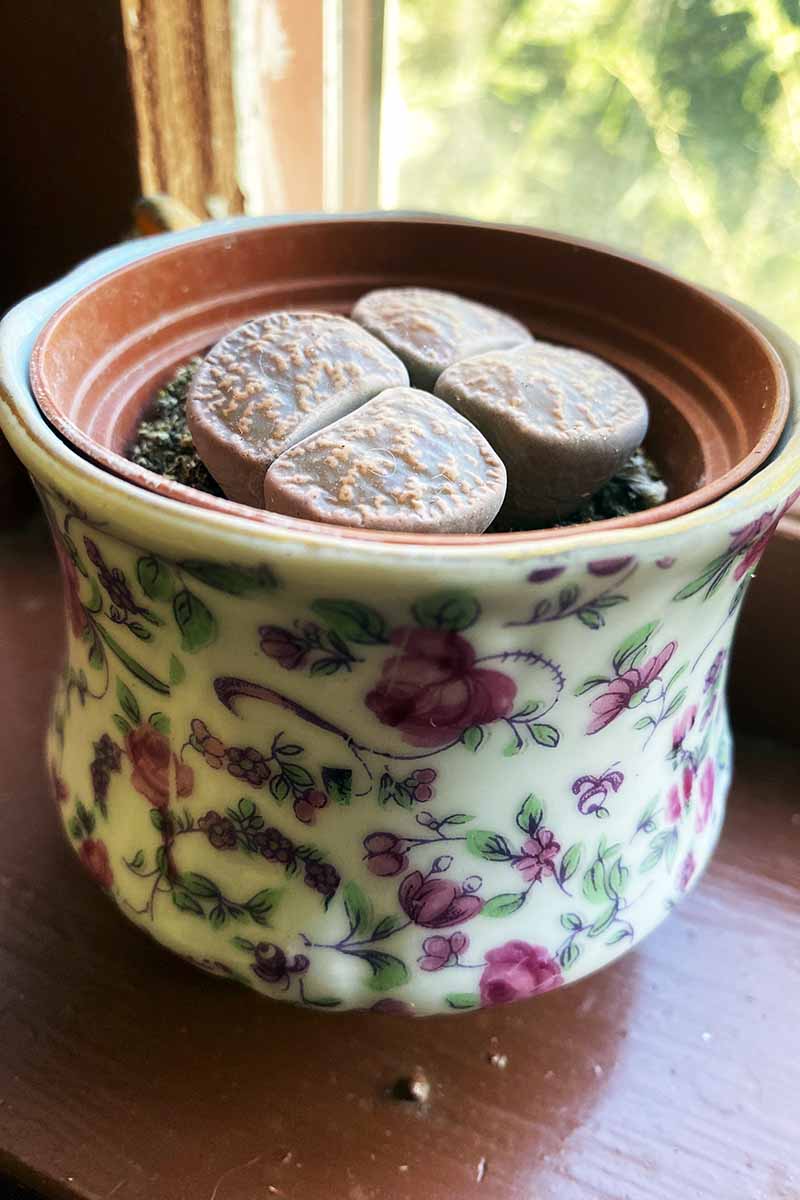
Lithops blend in with surrounding stones.
You will for sure want to learn what is call for of you before you acquire one of these – or as presently as possible after bringing a lithops home !
Ready to determine out how to produce and give care for living Stone ? Here ’s what we ’ll insure :
What You’ll Learn
What Are Lithops?
If you were to ask a minor to make a drawing of a plant , you ’d probably get an icon of a theme with big green leaves .
The subject of our clause could n’t be further by from this verdant visual sensation of planthood – and most living stones are not even green !
There ’s a reason for that .

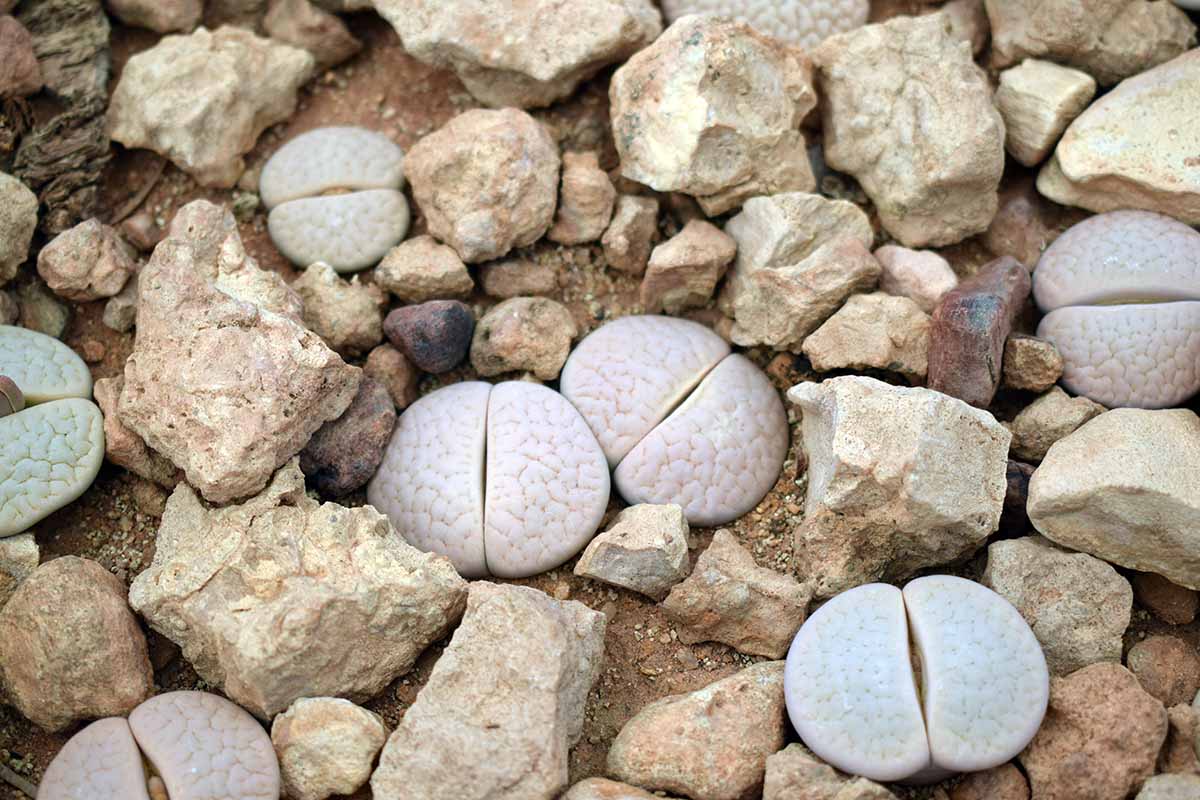
Lithops blend in with surrounding stones.
These succulent works camouflage themselves as stones , appearing in very muted colour to avail them blend into their environ natural home ground of rocky , gravelly terrain .
Referred to as “ mimicry plants , ” lithops have develop this growth habit to hide from hungry animals track down for leafy green solid food .
This low - profile increment habit also allow lithops to protect themselves from their harsh climates , as the volume of the industrial plant is place underground .

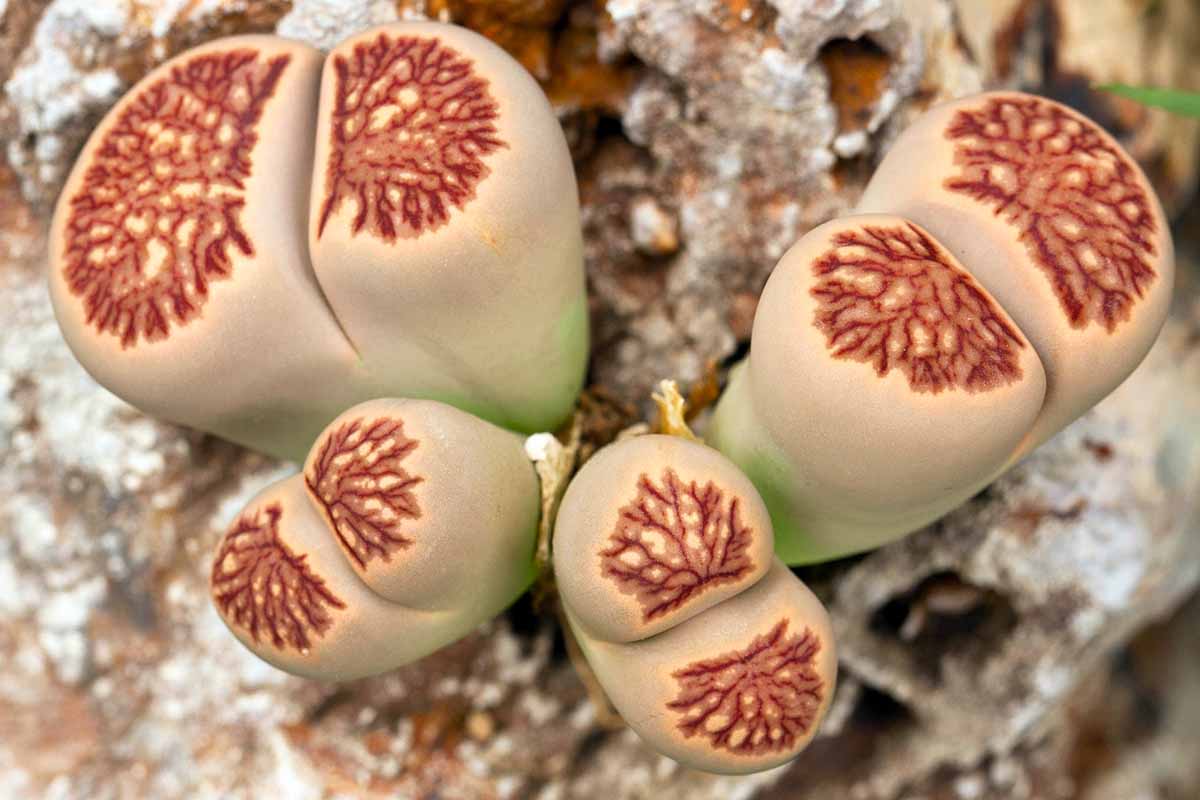
Lithops Anatomy and Markings
flowering stone are unusual plants and describing them ask specialized term .
To well understand them and to appreciate the coming into court of the unlike live on Isidor Feinstein Stone specie and cultivar , it ’s worth taking the clock time to memorise what these full term have in mind !
Bodies or Heads
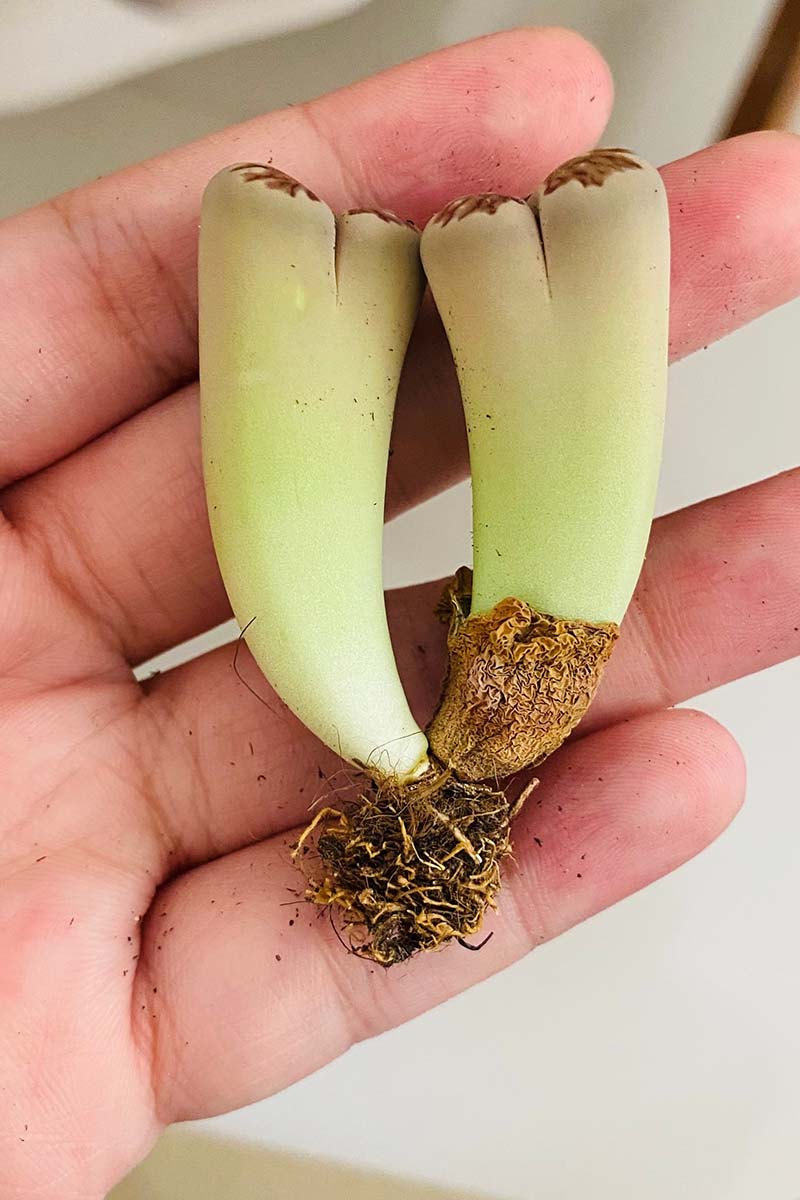
The “ dead body ” is the sarcoid part of the lithops plant , not include its roots . Part of the eubstance grows underground , while the rest is visible aboveground .
The body of these plants – made up of two consolidated leaves – are about two inches tall , more or less , and are shaped like center , three-fold wedge , or turn back cones , with the pointy , down remainder giving way to diminished root .
Depending on the lithops species , only the top half - inch or so of the body may go forth from the ground , while some are rather elongated , with more of the plant above the soil parentage .

The bodies of these succulent graze in width from about half an in to an column inch and a one-half all-inclusive , depending on the species .
The term “ head ” is another terminal figure for body , but usually refers to the part of the works that is above solid ground .
Some living stone mintage produce just one head per plant during their integral lives , while others may produce clumps made up of dozens of heads .

Lobes and Faces
Lithops bodies are made up of two slurred , fleshy , fused leaves , called “ lobes ” – two lobe make a head .
The lobe of some species are adequate in sizing , while others are slightly ( or quite ) asymmetrical .
Additionally , there is magnetic declination as to the depth of the cranny between the two lobe – with some having a shallow crack and others a deep one .
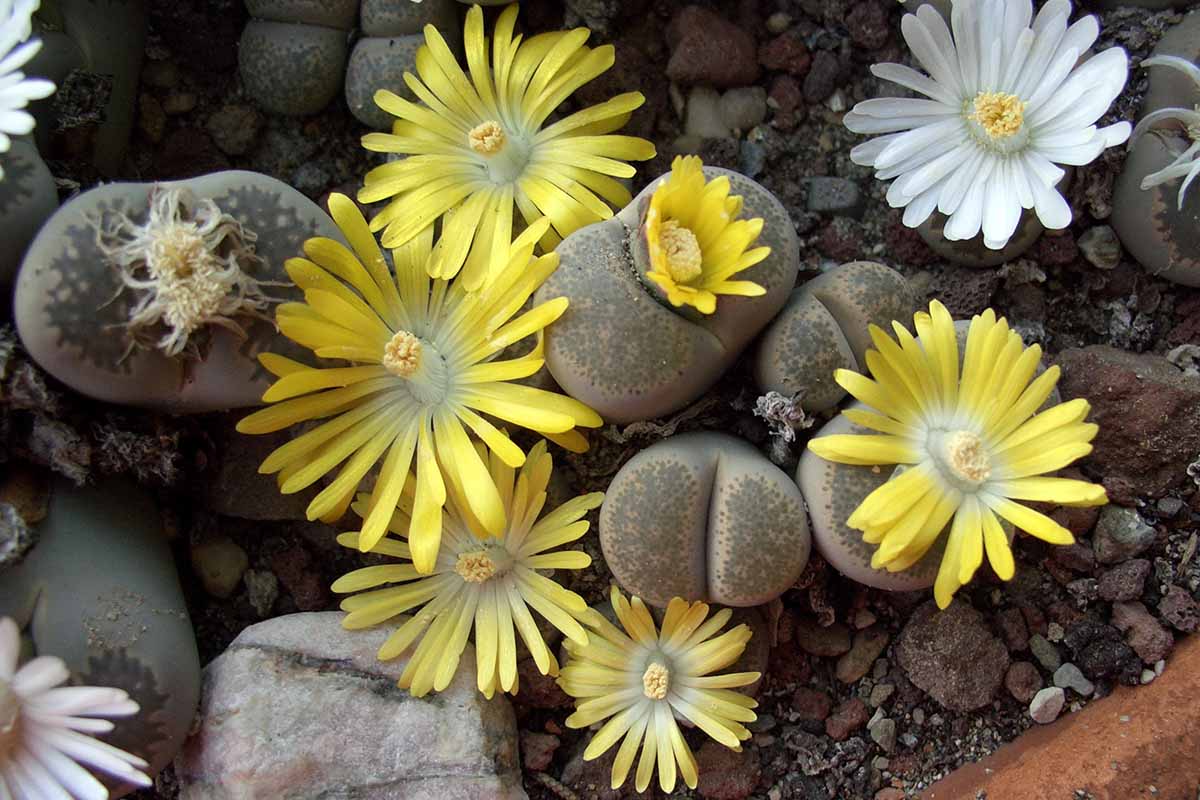

Likewise , some lobe uprise tight together ( these are describe as “ wealthy facial expression ” ) , while others are diverging , with a wide gap between the two lobe .
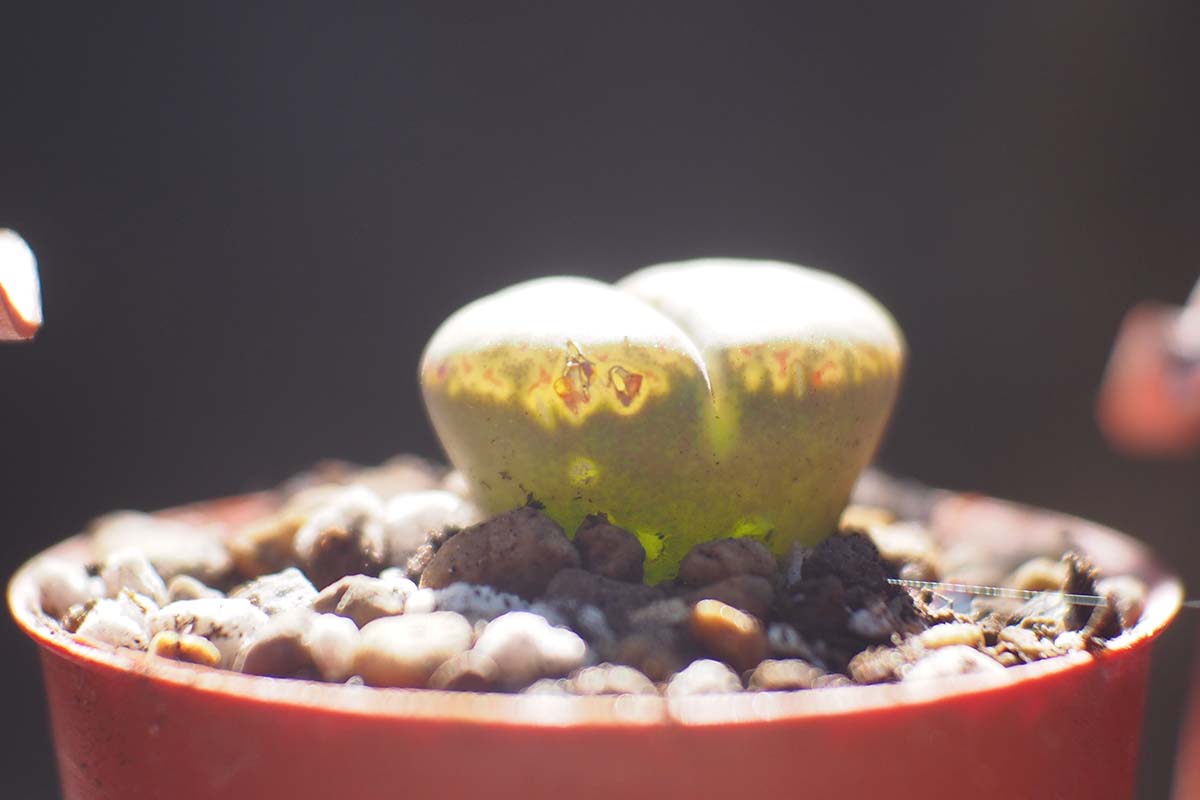
The tops of the survive stone lobes , when view from the side , can be either more or less flat , or round out .
mark that this appearance can change when the plant is well - water , in which case the lobes may become more convex , or when the plant is thirsty , when the tops of the lobes may become slightly concave .

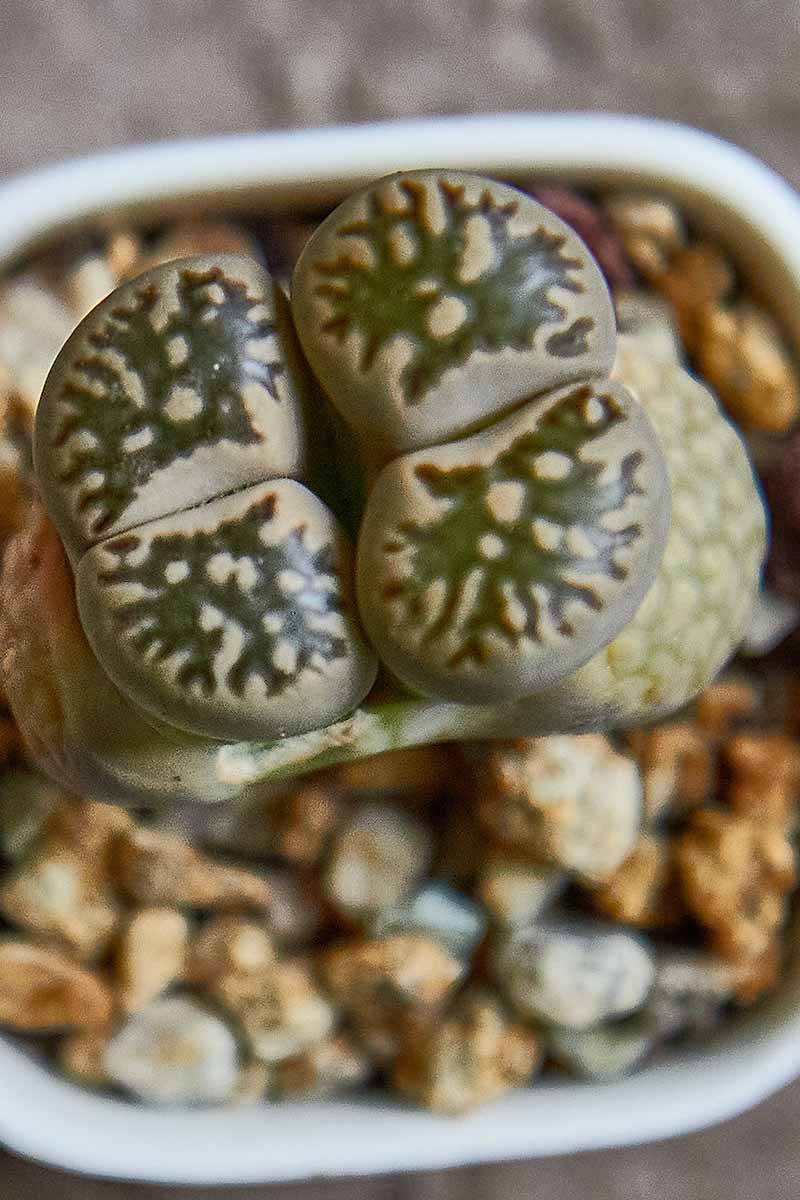
Looking down on them from above , lithops headway are more or less round or oval mold , and see from this angle , each folio is known as a “ face . ” Each head or body has two faces .
These face can have half - circuit , half - ellipse , kidney , or even slightly orthogonal shapes .
Some faces have smooth surfaces , others are rough and can be textured with furrow , swelling , warts , line , or endocarp !

Fissures and Molting
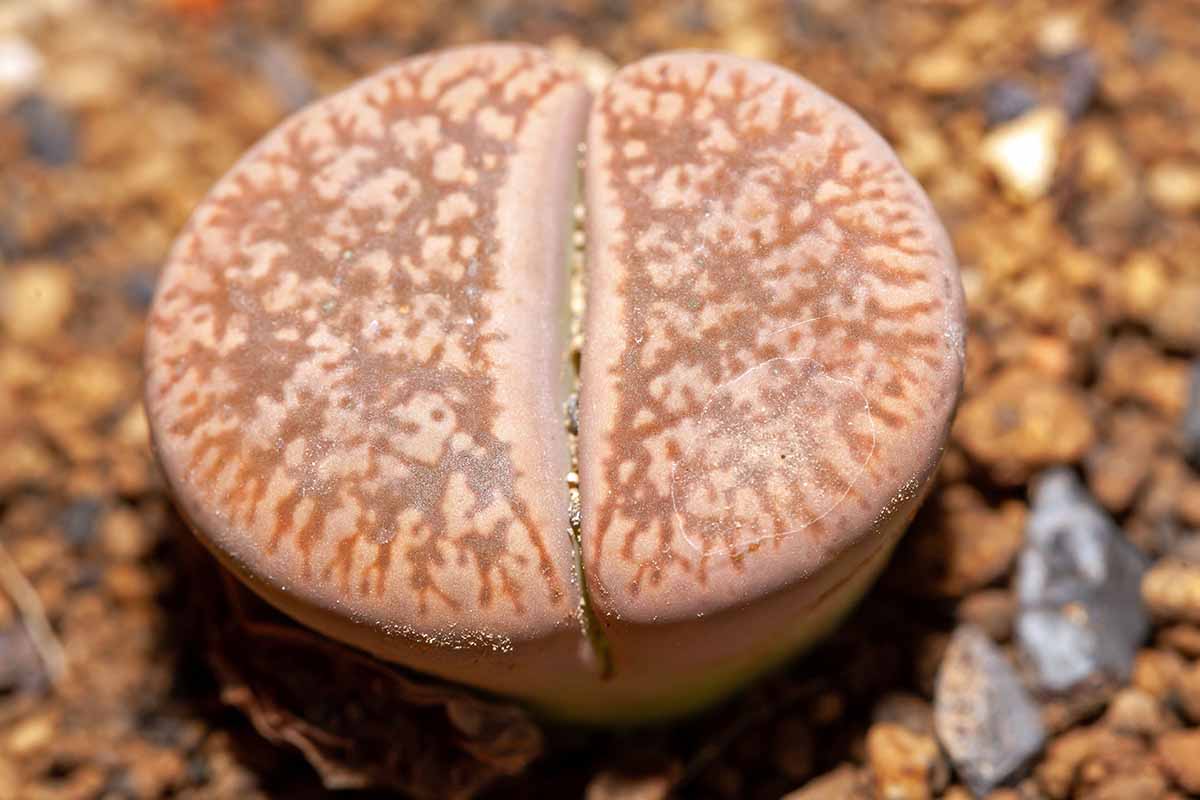
Both bloom and new foliage issue from the scratch ( usually referred to as the “ fissure ” ) between the two fused leaves , each at different time of year in the year – most lithops species produce flush in fall and new leaves in springtime .
When raw leave-taking emerge , the body give way through a cognitive process called “ moult ” ( similar to that of animals ) , in which the one-time leaves dry out out and are throw away to make direction for a new set of leaves – or sometimes a double set of leaves .
This answer in some live stone species eventually stimulate many heads on one plant .

Flowers
As for lithops blooms , only one prime is produced per promontory , and this is held facing the sky on a very short stalk .
efflorescence are daisy - like , and usually sensationalistic or white – or yellowandwhite . In some species , flower can be shades of bronze or garden pink .
These emerge in fall in most species , and in bright sun , usually at noon .
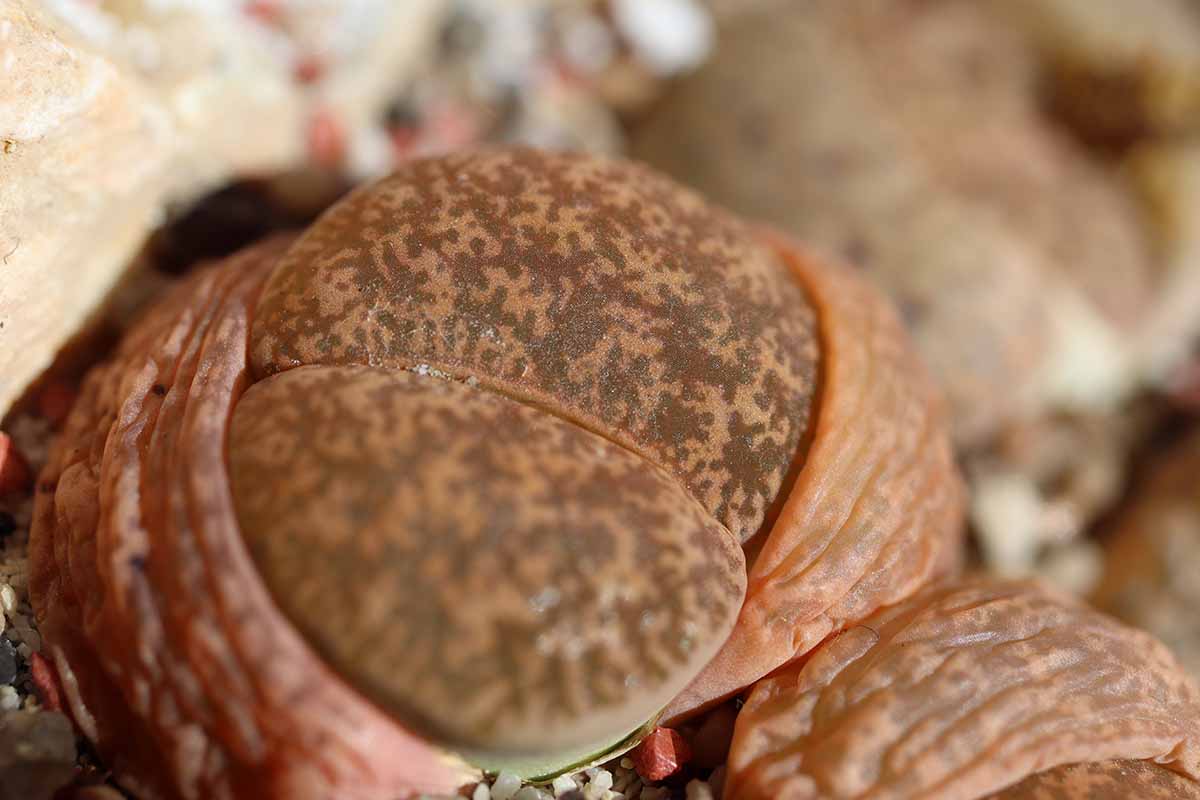

Windows
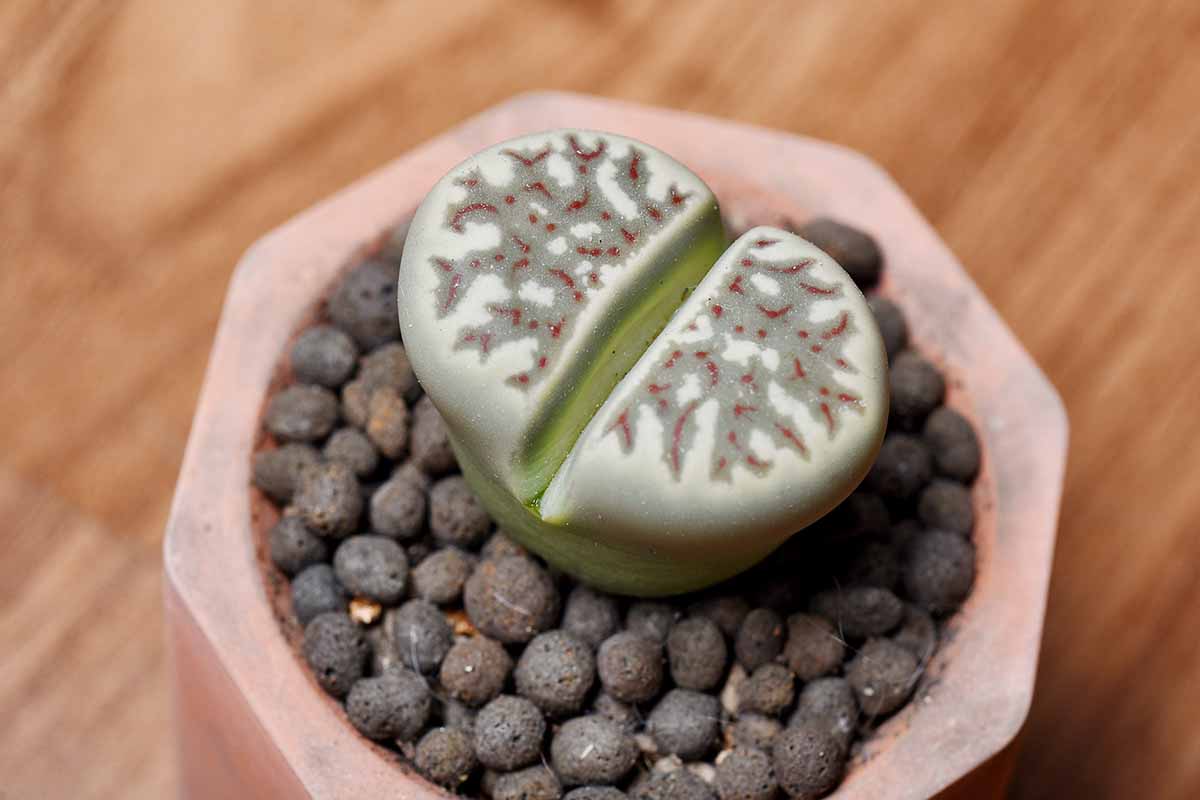
To make up for keeping their leaves mostly underground , the top part of each lobe has what is recognise as a “ window ” – a semitransparent section of the fount .
Windows are also sometimes called “ seas ” or “ lakes . ” These window allow light into the plant , where photosynthesis take place .
If you were to cut a lithops in cross section from top to bottom , you ’d find translucent tissue inside the leaves below the windows , as well as greenish tissue lining the inside of the body .

This windowpane is more visible in some mintage than in others . Some are unobstructed and unsubtle , taking up most of the face – plants like these are sometimes referred to as having “ opened ” windows .
On the other extreme , some flowering stone have windows that are all opaque looking , often referred to as being “ absent . ”
Most lithops , however , have marking on them that obscure the windows at least pretty .
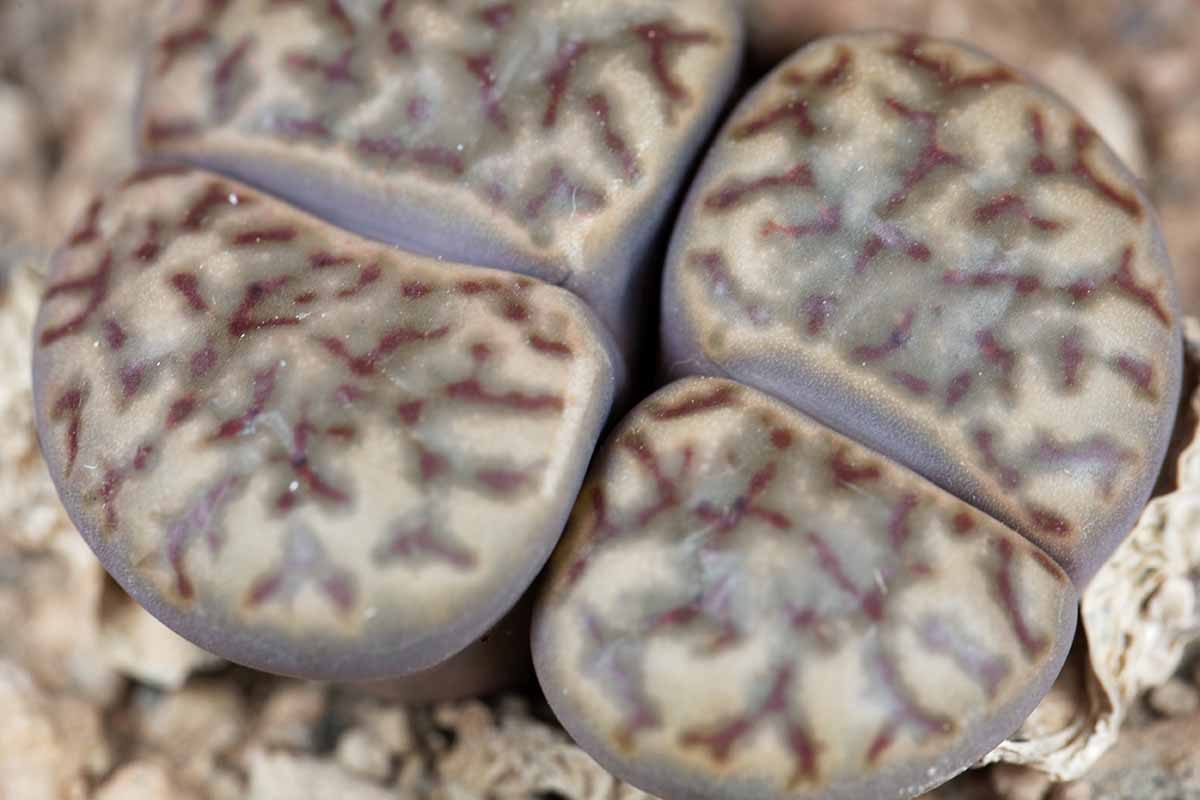
Sometimes small round dots of window are present among the unintelligible markings , and these are phone “ miniature windows . ”
There are special terms used to distinguish these markings .
While you don’thaveto have sex these terms to enjoy your plants , understanding what these words mention to can help you apprise what makes unlike species , subspecies , and diversity typical !

Ready to learn more about these markings ?
Islands and Peninsulas
Many living Stone have “ islands ” on their side . reckon that the window is a soundbox of water – the islands are opaque markings that seem to be adrift in this body of water system .
island can be large or small , few or numerous , and their edge can be more or less rounded , or quite notched .
As they do in actual bodies of pee , “ peninsula ” on live stone jut out from the edges of the face into the windowpane .

Margins and Shoulders
margin are bands of color around the window , or , in the absence of windows , along the edges of the face .
survive Harlan Stone plants sometimes have both internal and outer margins but not all species have discernible gross profit .
Sometimes be stone gross profit are the same color as the body , sometimes they are dissimilar colors .

The terminus “ shoulder ” is used to line the edge of the stone life face face , beyond the outer gross profit . The shoulder are sometimes yet another colour .
Channels
Some window have so many opaque scoring obscuring them that the window parts that are still unmistakable get a name change and are referred to as “ channels . ”
channel can be narrow-minded or wide , are sometimes furrowed into the case ’s open , and are sometimes line with additional markings .
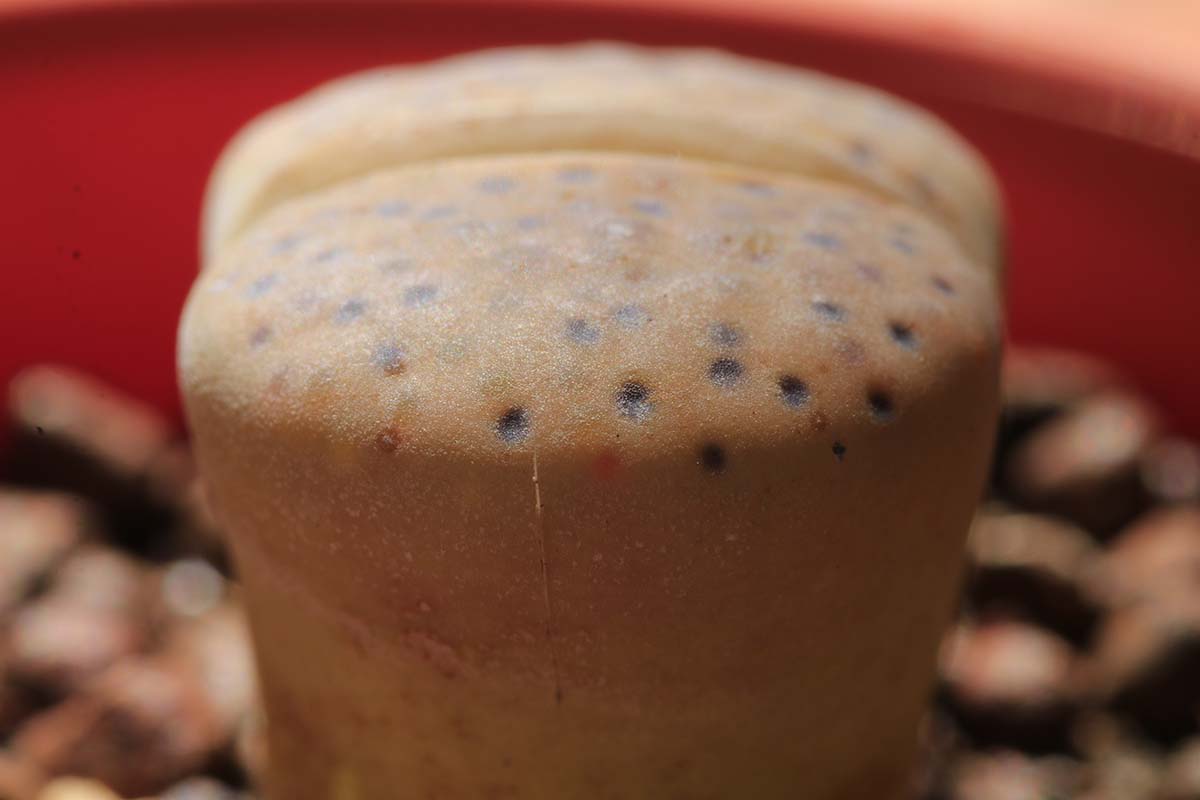
Dusky Dots
Some coinage have what are call “ dusky DoT ” dress their surfaces .
These can be indented , flush with the surface , slenderly elevate , or very much in relief , in which eccentric they may be referred to as “ wart ” or “ zit ” depend on how enceinte they are .
Dusky dots can be colored grey , dark green , or brown .

While there are sometimes small , window pane mold windows on the face , those are translucent while swarthy dots are unintelligible .
Rubrications
Many species of lithops have dingy blood-red patterns on their cheek , cry “ rubrications . ”
Rubrications can be in the form of lines , dots , checks , or star topology , and they often describe channels , creating either a connected connection of shape , or a busted connection .
mark that not all of these features are found on each works . The combination of these marking along with their anatomical characteristic is what allow these miniature marvels to be distinguished from one another !

Cultivation and History
Lithops hail from southerly Africa , with population aboriginal to Botswana , Namibia , and South Africa .
In the wild , they uprise in habitat composed of bare rocky ground , dry grassland , and scrubland . The soils in their aboriginal environments be given to be jolty and sandy .
These succulents have adapted to condition with small rainwater . Their aboriginal region receive an average of 20 inches of rain per twelvemonth or less .

Populations of stone plant in some placement get less than four inch of rain a yr , and some are watered primarily by fog and mist .
However , most specie arise in climate that are red-hot in the summer , with autumn pelting , and coolheaded or cold winters .
Lithops are members of the ice plant family , or Aizoaceae – also known as the “ common fig tree marigold ” family .

phallus of this family includeice plant ( Delosperma lehmannii ) , New Zealand spinach plant ( Tetragonia tetragonioides),andbaby toes(Fenestrariaspp . ) .
Relatives from this fellowship include additional mimicry plant which may be attractive to succulent collectors – such asConophytum , Dinteranthus , andPleiospilosspecies . The members of thePleiospilosgenus are known as “ disunited rock plants . ”
The genus nameLithopscomes from the Greek and means “ stone face ” or “ resemble Harlan F. Stone . ” These succulents are also sleep with as “ pebble plants ” or “ living stones . ” For reasons that should need no explanation , some also call them “ buns plant . ”

The subject of our article , as well as some other member of this house are often name “ mesembs , ” which is short for Mesembryanthemaceae , a synonym for Aizoaceae .
Mesemb is commonly used as a synonym for the expression “ mimicry works ” – both of these term are used for other phallus of the Ficus carica marigold family as well as stoneface .
Speaking of plant families , lithops were first class taxonomically in 1922 , making them comparatively late arrivals to the houseplant scene .

There are around 37 mintage in theLithopsgenus , as well as many subspecies , naturally occurring change , and cultivar .
Currently lithops populations are under increasing threat in the wild due tohabitat expiration and poaching .
While plant assembling is a fun hobbyhorse , be certain to limit your purchases to specimens that are nursery grown rather than incur through poaching wild specimens .

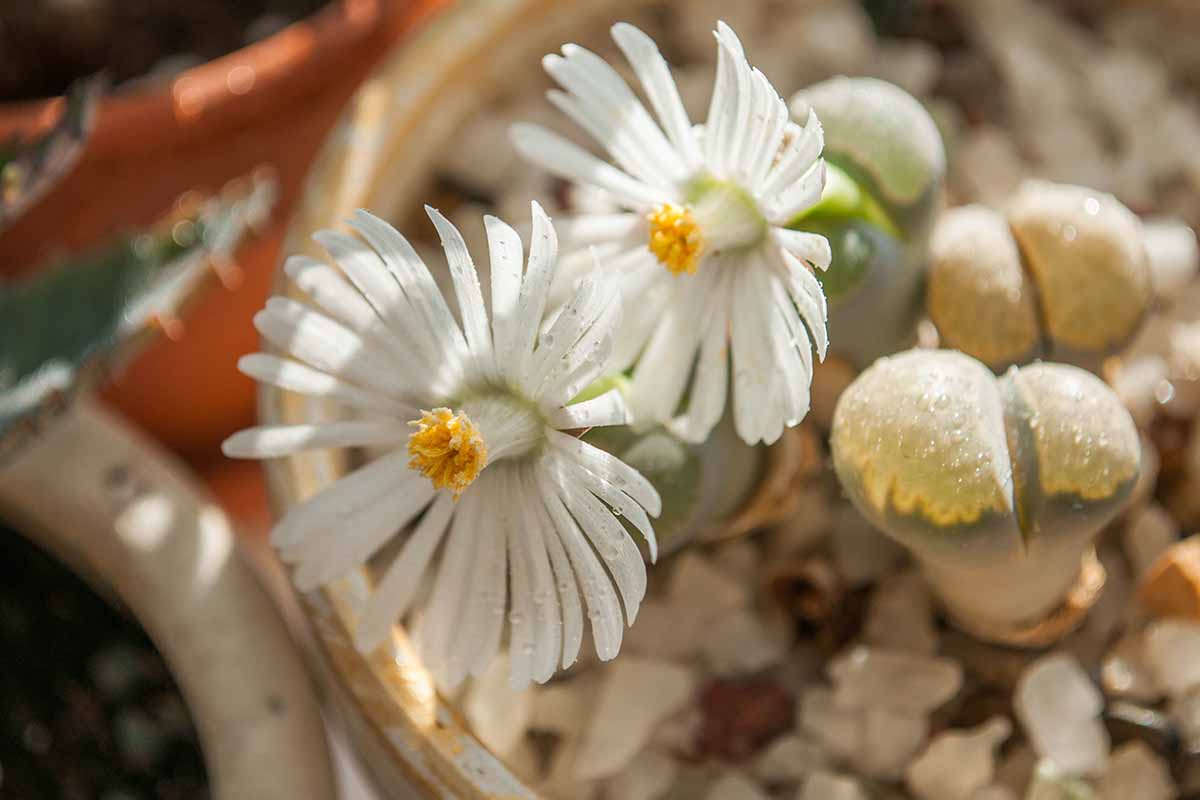
Interestingly , these petite succulents can live to be quite sure-enough in cultivation – up to 50 years – joining the social rank of other long - exist houseplants such asChristmas cactiandhoyas .
While succulent enthusiasts can grow these plants indoors , lithops can also be produce outside twelvemonth round out inUSDA Hardiness Zones9b to 11b , provided you’re able to protect these drought tolerant plant life from receive too much H2O .
Lithops Propagation
There are two ways to spread lithops – from seed and by dividing plants , both of which are easy methods . Let ’s front at each of these :
From Seed
Late spring , belated summer , and early fall are all sound time to pass around live stone from seminal fluid .
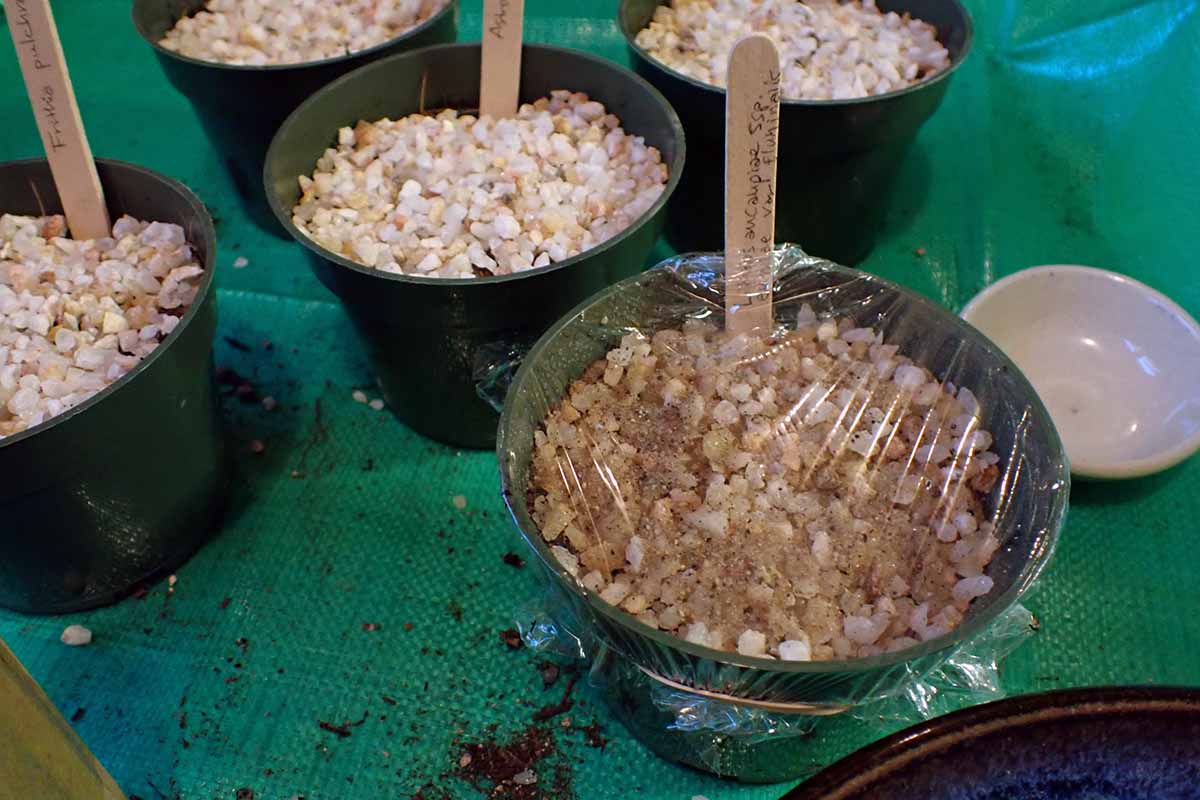
Here ’s what you ’ll demand for this project : stone-face seeds , ok grit , modest river rocks or coarse silicon oxide sand , three- or four - in nursery pots or a extension tray , a spray feeding bottle filled with water supply , a humidity covered stadium , and grow medium designed for cactus and succulents .
While adult lithops can be grown in a gritty , mostly mineral found intermixture , seedlings need a medium with a bit more moisture retention .

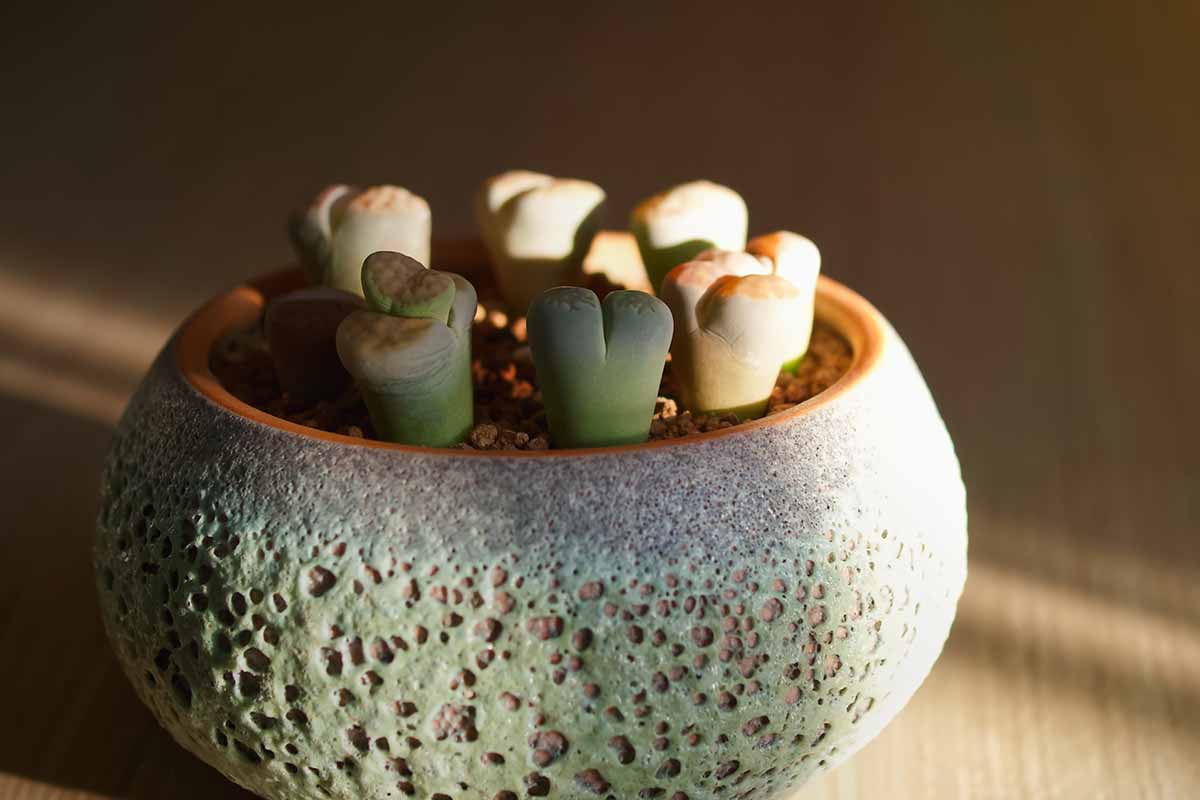
An idealistic premix for this purpose is to unite one part coarse silica sand with two parts cactus and succulent potting medium , Tank’s - Pro Cactus and Succulent Mix , available in a 1.5 cubic foot bagvia Arbico Organics .
Tank ’s Pro Cactus and Succulent Mix
First , fill nursery lot with growing medium , leaving an inch and a one-half of blank between the top of the growing mass medium and the lip of the stool .

Once you have fill the baby’s room pots or tray with the growing sensitive , go in front and irrigate it down .
Next , on top of the growing intermediate berth a half - column inch layer of small-scale river rocks or rough-cut silicon dioxide sand , such as this coarse silica sand available from Miukada in 3.3 Irish pound bagsvia Amazon .
Now mix the very tiny lithops seeds with about a tablespoonful of fine Baroness Dudevant – you may sow in 10 to 30 seeds per pot .

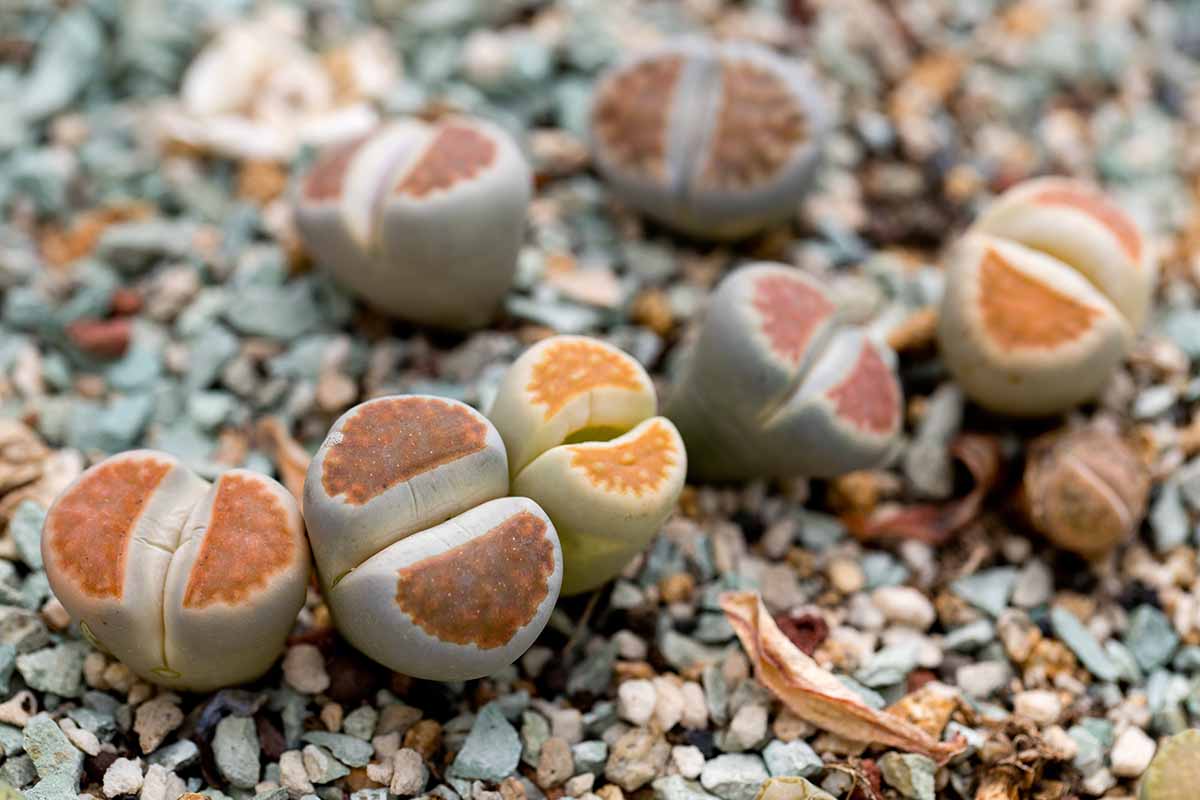
Sprinkle this sand and seed intermixture onto the layer of minor river rocks , then moisten the fine bed of sand with a few gentle mists from a spraying bottle .
Finally , cover the pots or tray with a humidity dome . you could use see-through plastic base for this , or you could brood the jackpot with plastic wrap . stop up the plastic wrapper or bags with rubber bands .
If you are using plastic wrapper or plastic bags , thump a few hollow in them with a toothpick to ply some ventilation .

mold plastic humidness domes usually descend with vents – you just take to open them slightly .
Locate the Mary Jane at elbow room temperature in collateral , smart luminousness to germinate . Although they ’ll be able to pull through in full sunlight once they are found , immature seedling will be scalded by direct sunlight .
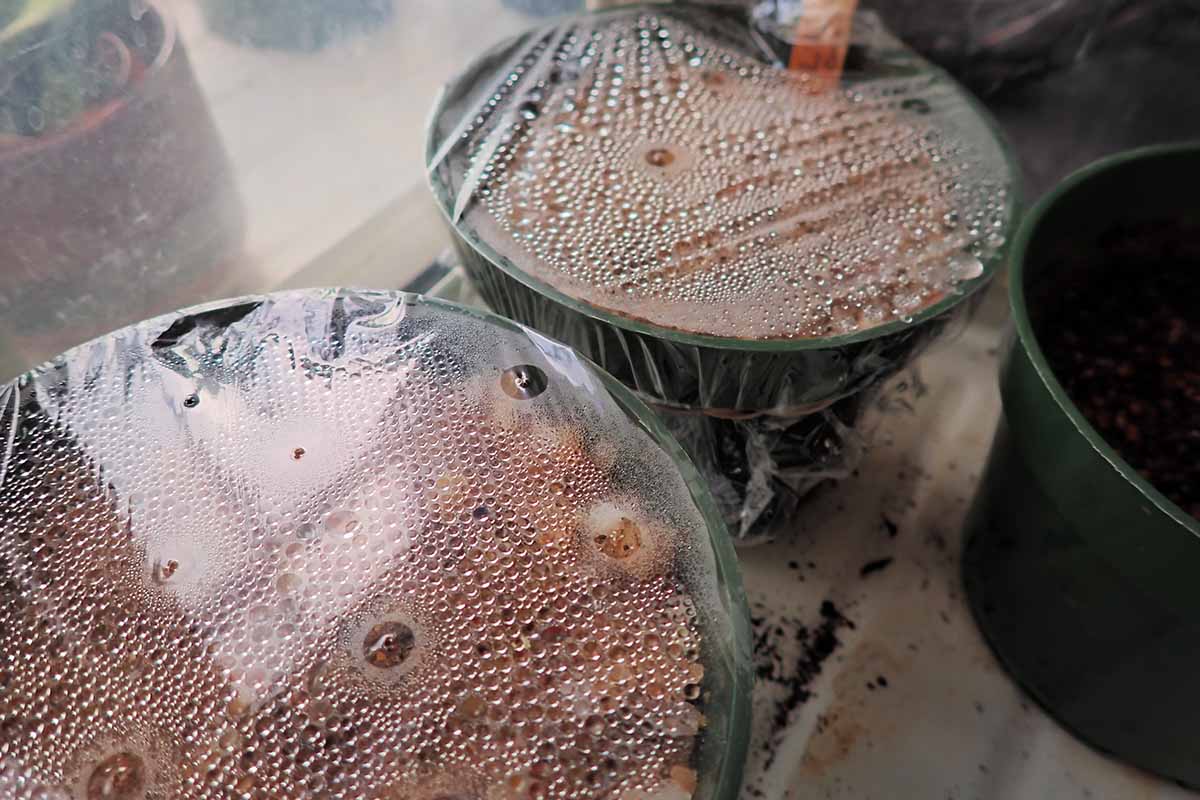
Keep an eye on the humidity dome , plastic bag , or plastic wrap covering your pots . When contraction disappears from this covering , it ’s clock time to water again .

Remove the covering and lightly spray the grow spiritualist with a water nursing bottle to keep the humidness high , then exchange the covering .
Expect sprouting to get down in five to ten daylight , though some seeded player will be much obtuse to germinate – some can take up to a year , so verify you sow in more than you need .
Two calendar week after germination , gradually transition the seedlings to ambient stipulation by removing the humidness dome for an 60 minutes the first mean solar day , increase the amount of time bring out to drier gentle wind each 24-hour interval .

irrigate the uncovered vernal seedling day by day by spray their growing mass medium with a spray bottle .
Two to three month after the seedling have germinated , increasingly increase the time between waterings , allowing the growing medium to dry out for a few days .
Wait 18 to 24 calendar month before transplanting seedlings to different peck .

instruct more about maturate succulent from seed .
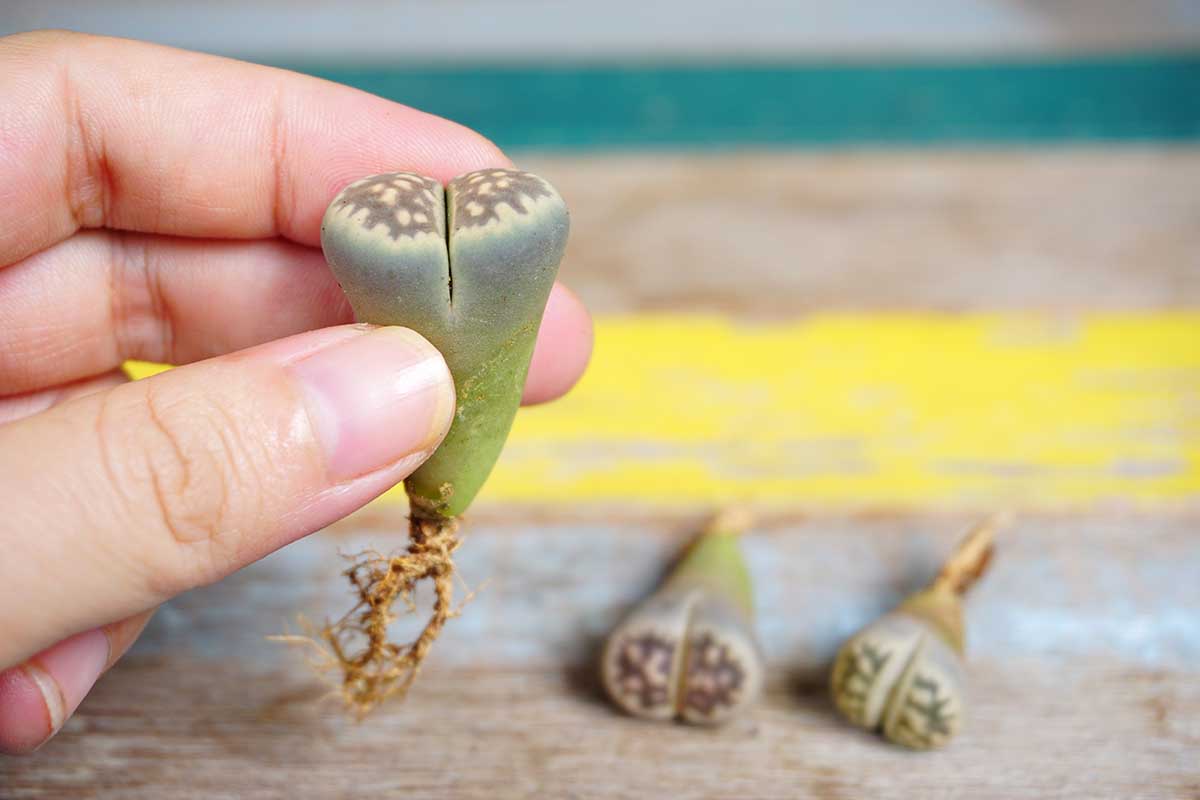
From Division or Transplants
While many succulent collectors valuate multi - headed lithops specimens , some houseplant parents may wish to experiment with separate these plant .
Living stones that have more than one oral sex can be propagated in this means .
call up , each head is made up of two leaves . Some species can form multi - headed plants , but not all .

So , just to be clear – do n’t break open a single head apart , instead , expect until a industrial plant has at leasttwoheads – or in other words , at leasttwosets of fused leave .
The best time to divide is after the flora has finished molting in spring .
Here ’s what you ’ll require : small gage , coarse silicon oxide sand , a butter knife , a sharp yoke of sterilized scissor hold orgarden pruners , and lithops growing average .
You ’ll ascertain more about creating a suitable grow metier for know stones later in the clause , so keep reading to ascertain more !
When you ’re ready to divide , first prepare small pots for transplanting , such as these two - and - a - half - column inch ceramic pots with bamboo saucers , available via Amazon .
Pack of 6 Glazed Ceramic 2.5 ” x 2.15 ” Succulent Pots
Fill the batch with growing medium , exit an inch of space at the top .
Remove the stone-face from its pot , then softly remove the growing sensitive from the plant ’s tooth root .
Now , gently separate the heads from each other at the beginning , you may need to cut them aside with sterilized scissors or snips .
Remove any teetotal leaves or dead flush stem from the body , then allow the heads to dry for an 60 minutes before continuing .
utilize the butter knife to make a hole in the arise medium , and insert one of the heads into the muddle , root side down .
Wondering how inscrutable to plant the lithops in the soil ?
The soil level should reach just about to the leaf fissure . Depending on the species or cultivar , the plant will be mostly buried with only the top column inch or one-half in above the dirt line .
This will vary reckon on the species , so it ’s upright to know which type you have !
stop up by add a half - inch layer of coarse silica sand or fine river rock to the surface of the growing medium as amulch . This will help keep the upper portion of the industrial plant body wry .
Repeat the unconscious process with any additional head teacher , or but return the parent plant life to its pot , fill in with extra farm culture medium if needed .
For stone plant that have been part , give them two weeks after division until allow for them with water .
After two weeks have passed , water them every 10 day for the next two to three months , at which point they should be well - root in their new pots .
How to Grow Lithops
Lithops do n’t involve frequent precaution , but their care does involve more genial effort and planning than the average houseplant .
In this section you ’ll get general stone plant care that will work for the absolute majority of the species – there are some exception , however , so be sure to train specific directions for your chosen coinage .
Sun
Lithops can be develop in direct sun , or a mixture of lineal sunlight and vivid , indirect light .
Aim for at least four to five hours of unmediated sun per daytime . This preference makes life I. F. Stone great prospect for life on a Confederate States - facing windowsill since they also do n’t take care cooling off a little at Nox .
However when move specimens grown in partly shaded conditions to greater direct sun photograph , do so gradually , otherwise they can be damaged by sun scald .
Also , if your menage gets specially hot during summer due to deficiency of airwave conditioning , decrease the plant ’s exposure to unmediated Lord’s Day .
you could do this by equip the windowpane with a sheer blank drapery which you close for part of the daytime or moving the works farther from the windowpane .
Climate
As for mood , lithops suffer a wide range of temperature , from high of 107 ° F down to sub - freezing temporary worker of 23 ° fluorine , but vulnerability to these extremes should be limited .
They will also be well-chosen in low humidity with good air circulation .
Water
The amount of water living rock will need reckon on how much direct sun they are receiving , how hot the indoor surround is , how moisture retentive their growing medium is – and the specie !
The most important thing to be intimate is that you should slip on the side ofunderwateringrather thanoverwatering .
In cosmopolitan , if your plant starts to shrink a bit and feel gentle , it might be meter to water .
However , before you plunk up yourhouseplant watering can , there ’s also a seasonal lachrymation schedule you ’ll take to know about first .
Late summer to fall is when the bulk of living stone postulate the most urine , before they begin to bloom and while flower .
Starting in late summer , water once every two to four weeks , allowing the grow medium to dry out between lachrymation .
Note that young specimen may not bloom , but still want to be watered during this period .
Whether it flowered or not , in wintertime most stone-face species go through a dormant geological period and it ’s important to withhold water during this season . Or at the most , if the plant is shrink , offer a very light lachrymation of a few drops or a light misting of the growing medium .
In late wintertime or other spring a experience stone will start to moulting , shedding its old skin to produce a new duet of leave , or two new pairs of leafage .
It ’s important not to water at this time . The new growth will take the wet it needs from the one-time growth , leaving the previous leaves to flex into a thin , desiccated skin .
This process is necessary for the new growth to emerge properly – if you irrigate , you ’ll prevent the erstwhile growth from drying out .
Once the living stone ’s old leaves have completely dry out up , begin to water supply again , approximately every two weeks , permit the maturate medium to dry between waterings .
When shape start to get hot in summer , the plant will experience another dormancy period , and watering should be withheld or at least , decreased . urine only if the plant is shriveling , and if it ’s very hot , tighten direct sun exposure somewhat as well .
Begin water again in late summer – and continue the lithops ’ yearly cycle .
If you ’re having a intemperate time keeping track of the watering agenda for this flora , consider keeping annotation in the calendar section of agardening journal .
How do you know if you ’re water a stone plant too much ?
Overwatered life stones can develop diseases and sometimes even burst – but the first mansion you ’ll point out is extension .
However , mark that some mintage are naturally elongated , so it pay to know the distinctive equipment characteristic of the species of stone-face you ’re growing so that you may aright tell apart when something proceed haywire !
Once a plant has been affected by overwatering , there is little that can be done to come back the plant to its former glory , making proper lachrymation your first step in keeping these succulent healthy .
Soil
Of of course , these succulents are also less probable to hurt the personal effects of too much water if they are cultivated in the good character of growing sensitive .
Since lithops ’ native habitat consist of rocky , gritty , arenaceous territory , you ’ll want to sample to mimic those condition when choosing a grow medium .
invalidate growing medium that containnon - renewable peat , which is not an appropriate ingredient for these succulent anyway .
To get a line more about whatprofessionallithops growers use in the way of grow mediums , I reached out to Jane Evans , co - owner of Living Stones Nursery in Tucson Arizona , a line of work which only trade to local customers .
Evans told me that their stoneface potting admixture is essentially 50 percent cactus mixture and 50 pct pumice .
Pumice is a great horticultural element to have on mitt when your beloved for houseplants is turn into – well , let ’s call it ahobby .
you may purchase an eight - quart base of horticultural pumice stone from Tank ’s Green Stuffvia Amazon .
So keep this 50:50 ratio in mind when creating your ownsucculent pot soilfor transplant , dividing , or repot your living stones . A ready - to - use , commercial-grade cactus and succulent soil in itself isnot quiteright for stone life face . Additional grit is required .
Growing Tips
Maintenance
As we ’ve already discussed , the best agency to care for your live stone is to know what to carry from it throughout the seasons so that you may cater water at the appropriate time .
Here are a few other response to maintenance questions you ’re bound to question about !
Mulch
A mulch of crushed rock or coarse moxie is typically added to the top of the produce sensitive . This keeps the survive stone ’s fountainhead dry and also helps to keep the plant erect .
If your lithops arise hobby is turning into a love , you might desire to choose gravel composed of the same types of rocks from your species ’ aboriginal habitat to leave it with five - star concern .
You might even go so far as to choose gravel that matches the vividness of their plant , to show off its artistry as a mimic !
Fertilizing
Fertilizing is not necessary with these succulent , which acquire to flourish in poor grime . Some professional grower fertilize oft , however , and others do so very seldom or not at all .
One option for home agriculturalist of living rock is to offer a aristocratic fertilizer when repotting , such as Dr. Earth ’s Succulence Organic Pump and farm Cactus and Succulent Plant Food .
Dr. Earth ’s Succulence Pump & Grow
It ’s available in a 16 - ounce heart bottlevia Arbico Organics .
Repotting
You wo n’t have to repot your live stone very often – on mean , only about once every two years if it needs spare way because it ’s create multiple heads .
When choose a spate , shallow mass are preferred , but they ’ll take to be at least two inches tall to accommodate the big part of the plant that grows underground . Those that are two to three and a one-half inches tall are idealistic .
you could repot lithops into modest , individual pot , or include them in a wide , shallow succulent smasher , either with other stoneface or with someeasy - care succulent buddies – just ensure to choose succulents with similar body of water and humidity need .
If your life rock still has plenty of room in its container , sufficient drain , and the container is to your liking , the plant will be well-chosen to stay there permanently .
However , older specimens with multiple head should be repot as their green goddess become crowded .
Encouraging Flowering
If you ’ve propagated a specimen from seed , do n’t expect flowering until the plant is two or three years erstwhile .
To boost flowering , ensure the works receive adequate sun .
Flowering is sometimes better on specimens grown in small , individual pots rather than panoptic dishes – though not all cultivator find this to be dependable .
Saving Seeds
If you ’re hope to produce living stone seeds for propagation , know that you ’ll need at least two specimens since they need to cross pollinate .
To spare seed , after florescence check that tobottom weewee . This is because water droplets hitting the top of the works will get the seed pods to open , release seed .
Allow pod to full mature and dry out before harvesting them , then store seeds for at least one yr before implant . Seeds will remain workable for many eld .
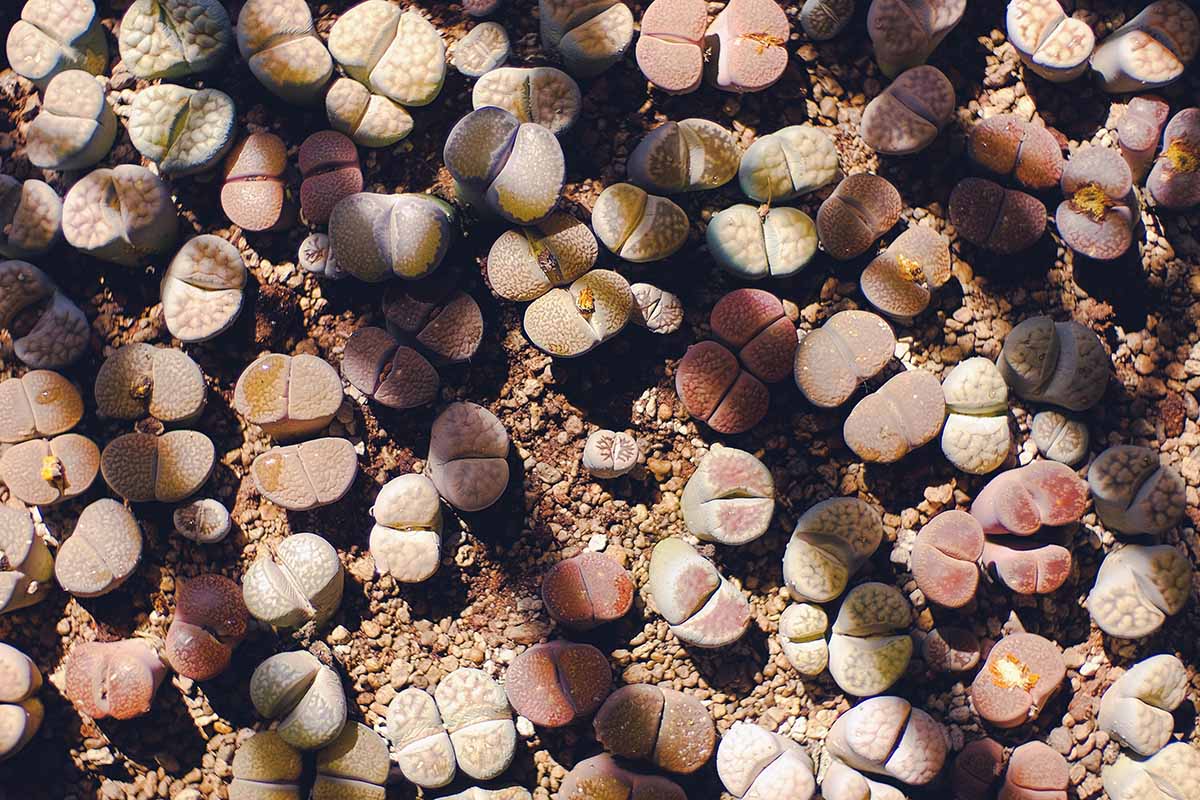
Lithops Species and Varieties to Select
There are many species , subspecies , course take place varieties , and cultivar of stone-face available to succulent collectorswithoutbothering with the loathsome practice of poach wild specimen . Here are a few of interest :
Karasmontana
L. karasmontanais a species that was bestowed with the Royal Horticultural Society ’s Award of Garden Merit in 2002 .
With a lot of variability , the species can come along in shades of brick red , beige , yellow , brown , pink , grey white , or grayish green .
This specie usually produces two to six heads , but can sometimes be found in ripe clumps of 12 or more .
Their faces have a jolty texture . Kids ( and the new at heart ) may get a kick out of these because some specimen can search rather like brains !
‘ Top Red ’ is a cultivar ofL. karasmontanathat has a ecru to gray body , and broad , furrowed , brick red channels .
Lithops Karasmontana‘Top Red ’ germ
require to try growing your own from germ ? you may buy 50L. karasmontana‘Top Red ’ seeds from Dichondravia Amazon .
Otzeniana
L. otzenianais a species that is usually found in an olive green semblance , but can also look in softened shades of pink , cream , or blue .
This be stone has a deep chap between its two leave-taking , and lobes that are slightly diverging .
With distinct margins around its translucent window , L. otzenianahas large rounded peninsula and islands frame its window .
L. otzenianabears yellow flowers with white centers .
Lithops OtzenianaSeeds
If you ’re quick to propagate your own , you ’ll retrieve pack of 15L. otzenianaliving Edward Durell Stone seeds for purchasevia Amazon .
Rubra
A cultivar ofL. optica , ‘ Rubra ’ is milklike pink to reddish purpleness in color , with translucent windows and smooth faces .
There ’s a very cryptic fissure between the two leaves , which gives this flora a different profile than many other stone life face species .
This living rock ’s beautiful brass are smooth with broad , dark royal or scarlet windows , and distinct margin . They ordinarily lack islands .
The heyday ofL. optica‘Rubra ’ are white , and often have pink tips .
Lithops Optica‘Rubra ’
Got your eye on these live stones ? you could keep them well within view – buy a three pack of one- to two - year - oldL. optica‘Rubra ’ stone life face via the Micro Landscape Design Storevia Amazon .
require More selection ?
There are many more type of living stones available to cultivate at plate or to admire from afar . Discover more inour guide to 37 different types of lithops .
Managing Pests and Disease
When it comes to pest and diseases , await healthy lithops specimens to stay pest barren .
However , be on the lookout formealybugs , plate , thrips , aphids , andspider mites . Fungus gnatscan be a problem for young seedlings which are kept in more humid atmospheric condition .
Rot is the only real danger of disease for this succulent , and can be forbid with right watering , the correct ground , and excellent drainage .
Read our article about rotting in succulent to acquire more .
Best Uses for Lithops
As discuss above , lithops make great windowsill plants , and would be lovely as part of atiny plantcollection . You might also consider including them in asucculent poof garden !
They can also be incorporate into wide-eyed , shallowsucculent planterswith other specimens , as long as the other works have standardised water and soil requirements .
Outdoors stone life face can be grown in sway gardens with cacti and other succulents in USDA Hardiness Zones 9b to 11b , provided they are give the right soil and moisture term .
Quick Reference Growing Guide
Lithops – Much More Fun Than a Pet Rock!
Living stones are unique and compact succulent that make first-class houseplants provided you have pot of sun and just the good amount ofrestraintwith the watering can .
And while for most of the year they may look like nothing more than preferred tilt , you ’ll know these living stones are quick to produce conjuring trick throughout the seasons – beautiful blossom , and sets of fresh novel parting .
need to keeplearning about cultivate cacti and succulent ? Have a read of these guide next :
picture by Kristina Hicks - Hamblin © Ask the Experts , LLC . ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.See our TOSfor more details . mathematical product photo via Amazon , Arbico Organics , Dichondra , Dr. Earth , the Micro Landscape Design Store , and Tank ’s Green Stuff . Uncredited pic : Shutterstock .
About
Kristina Hicks - Hamblin